News
Optical Superluminal Motion Measurement in GW170817
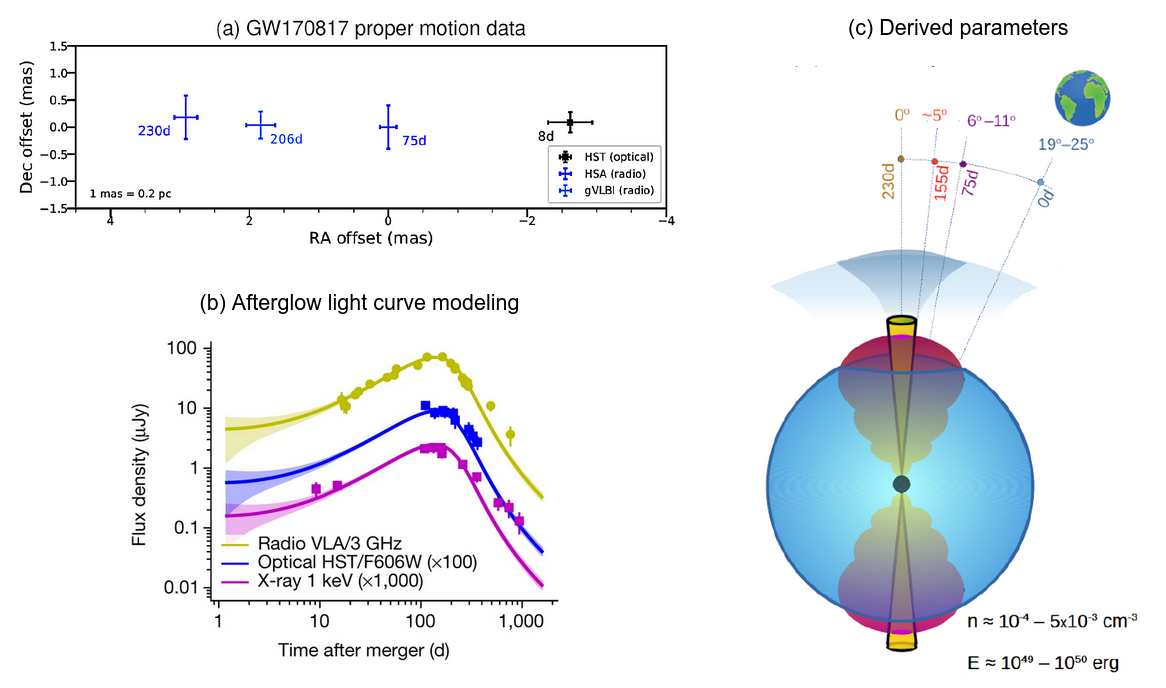
Posted 01 Dec 2022: We report on another superluminal motion measurement, at seven times the speed of light, leveraging Hubble Space Telescope precision astrometry and previous radio VLBI data for GW170817. We thereby obtain a measurement of the Lorentz factor of the wing of the structured jet, as well as substantially improved constraints on the viewing angle (19–25 degrees) and the initial Lorentz factor of the jet core (more than 40). Study presented in Mooley, Anderson & Lu 2022.
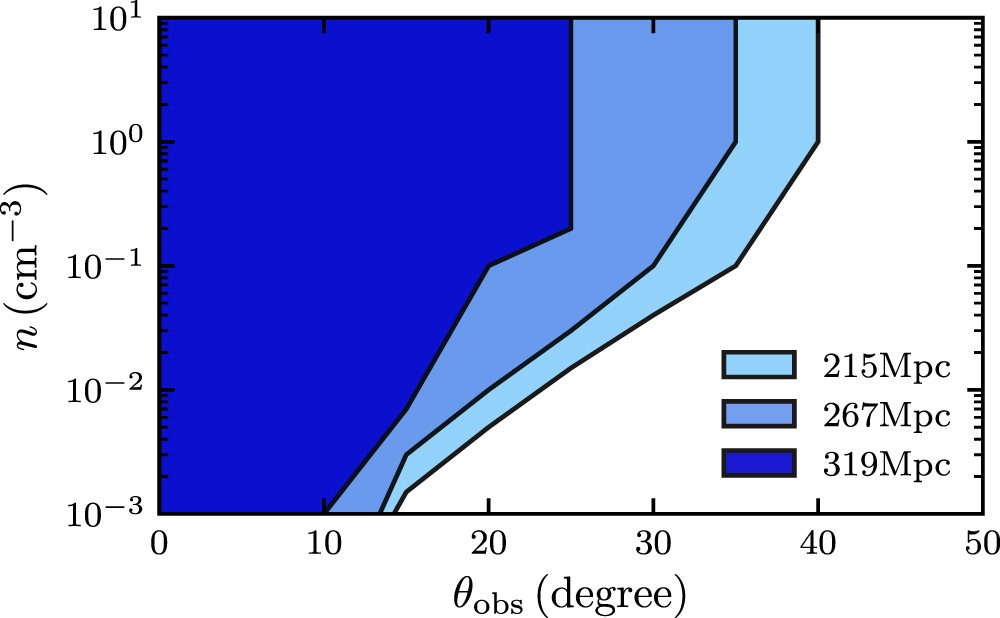
A comprehensive search for the radio counterpart of GW190814 with the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder
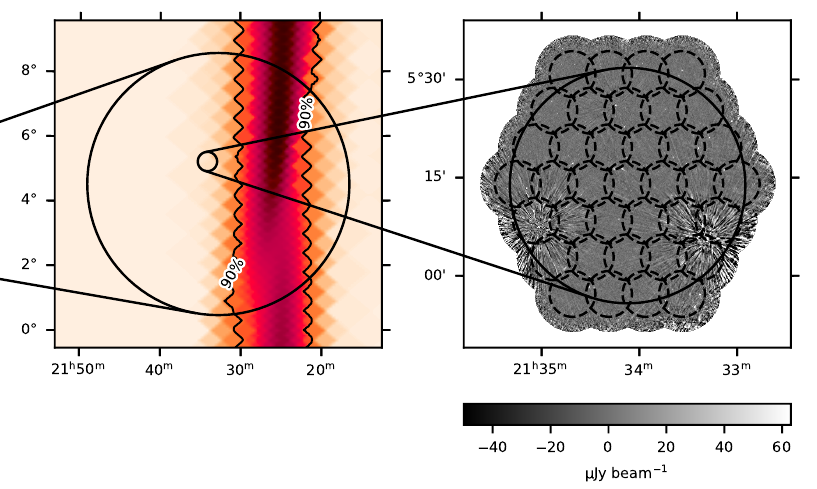
Posted Mar 2022: We present results from a search for the radio counterpart to the possible neutron star-black hole merger GW190814 with the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder. We find one radio transient, ASKAP J005022.3-230349, but conclude that it is unlikely to be associated with the merger. We use our observations to place constraints on the inclination angle of the merger and the density of the surrounding environment by comparing our non-detection to model predictions for radio emission from compact binary coalescences. Study reported in Dobie et al. 2022.
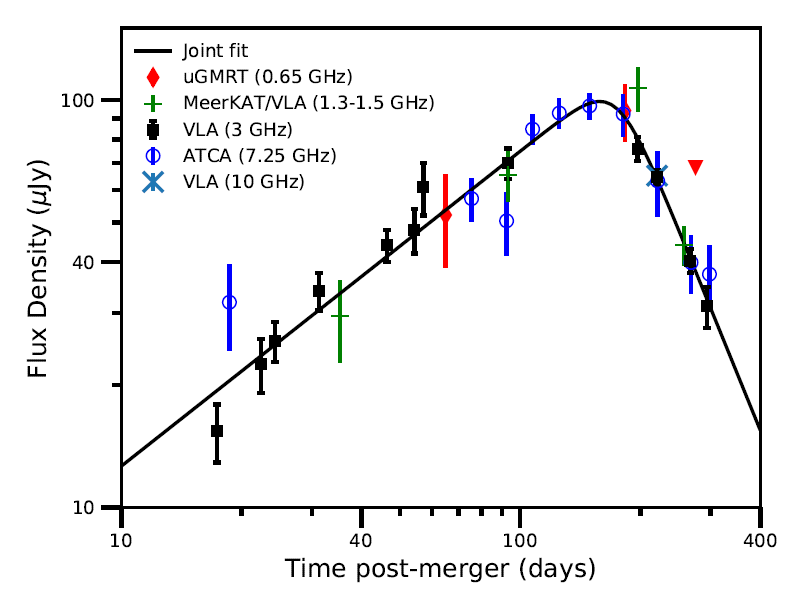
The Panchromatic Afterglow of GW170817
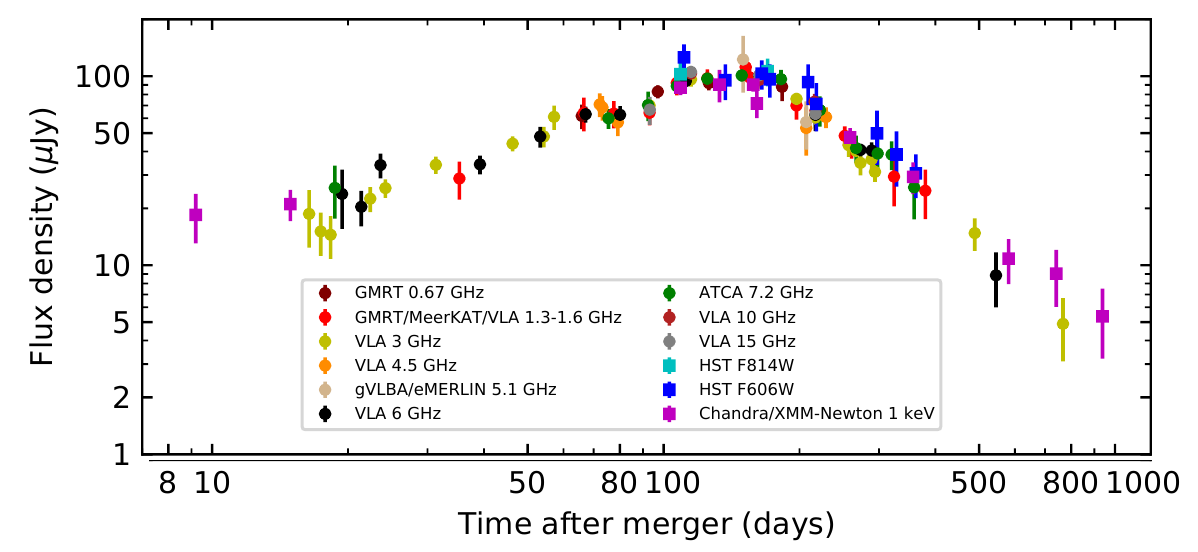
Posted 01 Dec 2021: We present the full panchromatic afterglow light curve data of GW170817, including new radio data as well as archival optical and X-ray data, between 0.5 and 940 days post-merger. Measurements are obtained for the light curve shape parameters, time of peak, magnetic field strength, electron power-law distribution and density of the circum-merger environement. Study reported in Makhathini et al. 2021.
Constraints on the dynamical ejecta afterglow of GW170817
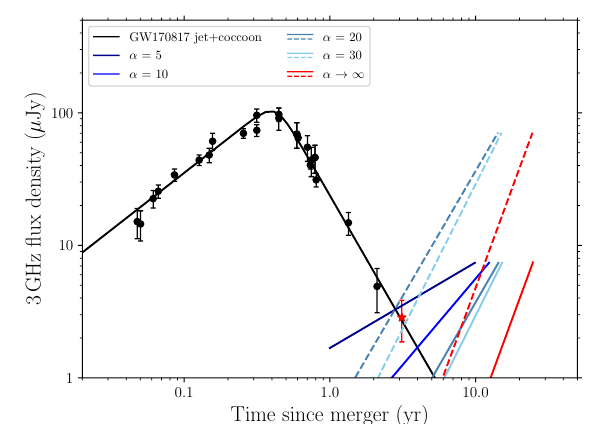
Posted 03 Jun 2021: We present the deepest radio observation of GW170817 carried out to date, where the afterglow is detected marginally at 2.86+/-0.99 microJy. The flux density is consistent with the jet decline model and rules out any new radio afterglow component such as that arising from the high-velocity tail of the GW170817 kilonova ejecta. Study reported in Balasubramanian et al. 2021.
Radio constraints for the possible Multimessenger Counterpart of GW191216
Posted 06 Dec 2019: Radio afterglow constraints were obtained for the possible multimessenger counterpart of the binary black-hole merger event GW191216. Study reported in Bhakta et al. 2021.
Limits on the radio afterglow of the high mass-ratio compact binary merger: GW190814
Posted 06 Dec 2019: Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP) observations have provided strong constraints on the geometry and local environment density of GW190814. Study reported in Dobie et al. 2019.
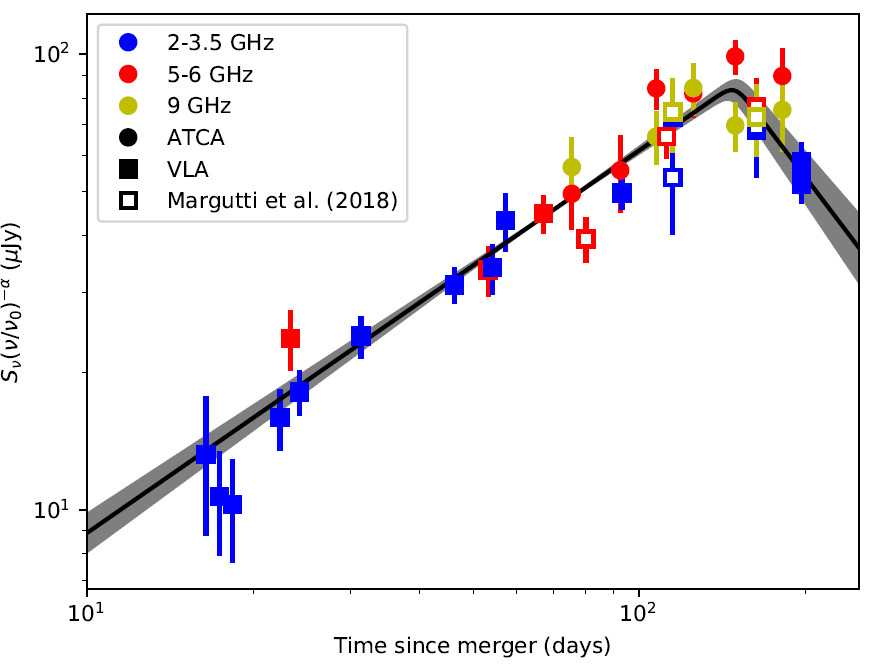
Steep decline in the radio light curve of GW170817
Posted 01 Nov 2018: Observations carried out with the VLA, ATCA, GMRT and MeerKAT telescopes indicate a steep decline of the radio light curve, which is a classic signature of a relativistic jet. Analytical calculation implies a viewing angle of about 15 deg and jet opening angle less than 5 deg. Study reported in Mooley et al. 2018d.
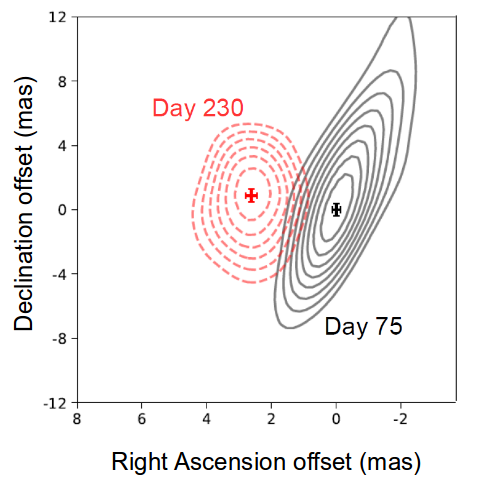
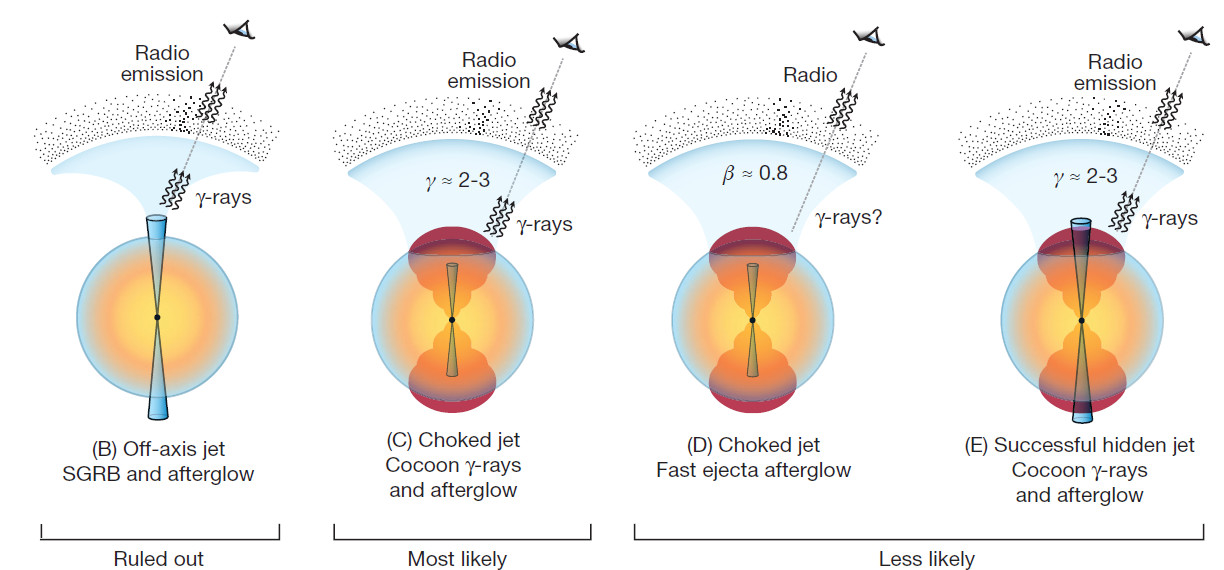
Decline in the radio light curve of GW170817
Posted 01 Sep 2018: Very long-baseline interferometry revealed a compact radio source associated with GW170817. The source exhibits superluminal apparent motion between 75 days and 230 days after the merger event. This measurement breaks the degeneracy between the choked- and successful-jet cocoon models. It indicates that the late-time emission was most probably dominated by an energetic and narrowly collimated jet (with an opening angle of less than 5 deg) and observed from a viewing angle of about 20 deg. This provides strong observational evidence linking binary neutron-star mergers and short GRBs. Study reported in Mooley et al. 2018c.
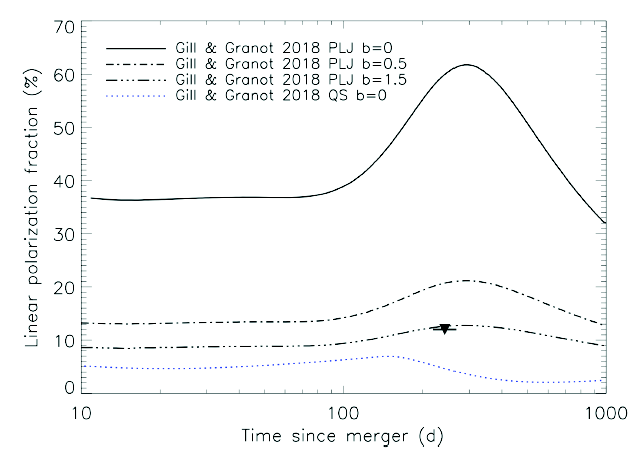
Radio polarization upper limit of GW170817
Posted 01 May 2018: Observations with VLA reveal that the linearly polarized emission in the afterglow of GW170817 is less than 12% at a frequency of 2.8 GHz (99% confidence). The polarization upper limit implies that the magnetic field is random in the plane of the shock. Study reported in Corsi et al. 2018.
Decline in the radio light curve of GW170817
Posted 21 Mar 2018: The well-sampled radio light curve of GW170817 obtained with the VLA and ATCA telescopes indicates a peak at 150 days followed by a decline in radio emission. The rate of decline is most consistent with mildly- or non-relativistic material and there is no clear evidence for an energetic off-axis jet. Study reported in Dobie et al. 2018.
On-the-Fly Mapping Applied to GW151226
Posted 19 Mar 2018: We applied a newly-developed On-the-Fly mapping technique on the VLA at 3 GHz in order to carry out a sensitive search for an afterglow from the Advanced LIGO binary black hole merger event GW151226. Study reported in Mooley et al. 2018b.
A wide-angle outflow in GW170817
Posted 30 Nov 2017: Using radio observations of GW170817, carried out while the optical and X-ray telescopes were constrained by the Sun, we rule out a simple off-axis jetand infer the existence of a mildly relativistic wide-angle outflow moving towards. Study reported in Mooley et al. 2018a. See also associated video.
A wide-angle outflow in GW170817
Posted 16 Oct 2017: JAGWAR discovered the radio afterglow of GW170817, the first neutron star merger detected by the LIGO-Virgo Collaboration. Study reported in Hallinan et al. 2017. JAGWAR principal investigator, Kunal Mooley, speaks about the discovery.